- What Is a crown ?
- Types of Crowns.
- What is a Bridge?
- How do Bridge Work?
- How are Crowns and Bridges Made
- How Long do Crowns & Bridges Last?
- Suggestions & Precautions
- F.A.Q.s
- Before and After Photographs
Crowns and most of the bridges are fixed dental prosthetic devices that are cemented on the existing teeth or implants. These can be taken out by a dentist only.
What Is a Crown ?
Crown is a fixed dental prosthetic device that is cemented on the existing teeth or implants. A crown or "cap" covers the entire surface of a damaged tooth. It not only strengthens a damaged tooth, it improves its appearance, shape or alignment as well. It may be placed on an implant too to give a tooth-like shape and structure for function. . Materials used to make a crown include—porcelain, ceramic, gold and metal alloys, and acrylic. Crowns made of porcelain or ceramic match the color of your natural teeth. As the alloys are stronger than porcelain they are preferred for back teeth.
You may be recommended crown as a treatment option:
- As a replacement of a large filling if there isn't enough tooth left
- Prevent fracture in a weak tooth
- Repair a fractured tooth
- Connect a bridge
- Cover up a dental implant, discolored or poorly shaped tooth, or tooth after root canal treatment
Types of Crowns
There are two types of crown--- prefabricated or custom made
Prefabricated crowns: These can be prepared from plastic or stainless steel. They are mostly used as a temporary restoration until a permanent crown is made. Rarely prefabricated crowns are used for permanent restoration. Prefabricated stainless steel crowns are mostly used in pediatric patients as a permanent restoration
Custom made crowns are made in laboratory using various materials and techniques or can be fabricated chairside using cad cam technique.Materials used to make crowns include metal [gold alloy, other alloys (palladium) or a base-metal alloy (nickel or chromium)], porcelain fused to metal (PFM), or ceramic. Crowns made of metals or PFM are tougher and preferred for back teeth. The life of a crown is at least 7 years, but they can last much longer (40 years or so). Some people may need endodontic or root canal treatment on the tooth before a crown. But everyone who needs a crown does not need a root canal treatment.
After a Crown
Following a crown there should be no discomfort or sensitivity in your tooth. However, if you have persistent pain or hot/cold sensitivity tell your dentist.
The gum line under your crowned tooth may appear to have a dark line especially after a PFM crown.
Remember that crowning of a tooth does not protect it from decay or gum disease. Crowns can last for the rest of your life. To increase the longevity of your crown maintain good oral hygiene. To maintain healthy teeth and gums brush with fluoride toothpaste (twice a day) and floss everyday and go for regular dental checkups and professional cleanings. Do not chew hard foods, ice or other hard objects to avoid damage to your new crown.
Crown can become loose or fall out. Food debris and bacteria can seep in from a damaged crown. The accumulation of food debris and growth of bacteria can lead to decay. Consult your dentist if your crown seems loose. If the crown falls out you can replace it temporarily and then consult your dentist. Your dentist may make a new crown or re-cement the old one itself on the tooth.
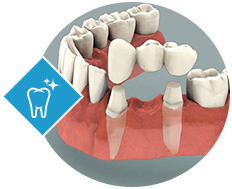
What is a bridge?
Bridges may be used to replace one or more missing teeth. They fill the space of the missing teeth. The bridge is attached or cemented to the existing natural teeth or implants around the unfilled space of the missing tooth/teeth. A traditional bridge has crown for each tooth on both sides of the space (the missing tooth/teeth) and false tooth/teeth in between the crowns. If the adjoining teeth on which the crown is placed are healthy and strong, they won’t need root canal therapy. But a small part of the teeth may need to be removed so that the crown fits well.
Porcelain fused to metal (PFM) or ceramics are most often used to make traditional bridges.
Besides the traditional bridge other types of bridges are-- Cantilever bridges, Maryland bonded bridge. Your dentist will recommend the kind of bridge you need after examining your teeth. At least two dental visits are needed to make a bridge.
Bridges last at least five to seven years or can even last for the rest of your life. To increase the longevity of your crown maintain good oral hygiene. To maintain healthy teeth and gums brush with fluoride toothpaste (twice a day) and floss everyday and go for regular dental checkups and professional cleanings. Do not chew hard foods, ice or other hard objects to avoid damage to the bridge.
How do Bridges Work?
If you have one or more missing tooth a bridge may be advised. Missing teeth can cause-
Remaining teeth to rotate or shift into the unfilled space of the tooth/teeth and cause bad bite.
Imbalance as a result of the missing teeth can lead to gum disease and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Bridges are commonly used to replace one or more missing teeth. They span the space where the teeth are missing. Bridges are cemented to the natural teeth or implants surrounding the empty space. These teeth, called abutments, serve as anchors for the bridge. A replacement tooth, called a pontic, is attached to the crowns that cover the abutments. As with crowns, you have a choice of materials for bridges. Your dentist can help you decide which to use, based on the location of the missing tooth (or teeth), its function, aesthetic considerations and cost. Porcelain or ceramic bridges can be matched to the color of your natural teeth .
How are Crowns and Bridges Made?
Before either a crown or a bridge can be made, the tooth (or teeth) must be reduced in size so that the crown or bridge will fit over it properly. After reducing the tooth/teeth, your dentist will take an impression to provide an exact mold for the crown or bridge. If porcelain is to be used, your dentist will determine the correct shade for the crown or bridge to match the color of your existing teeth.
Using this impression, a dental lab then makes your crown or bridge, in the material your dentist specifies. A temporary crown or bridge will be put in place to cover the prepared tooth while the permanent crown or bridge is being made. When the permanent crown or bridge is ready, the temporary crown or bridge is removed, and the new crown or bridge is cemented over your prepared tooth or teeth.
How Long do Crowns and Bridges Last?
Crowns and bridges can last for the rest of your life. But they can become loose or fall out. To increase the longevity of your crown or bridge maintain good oral hygiene. The bridge can be damaged if the teeth or bone holding it in place are affected by dental disease. To maintain healthy teeth and gums brush with fluoride toothpaste (twice a day) and floss everyday and go for regular dental checkups and professional cleanings. Do not chew hard foods, ice or other hard objects to avoid damage to your new crown or bridge.
Suggestions and precautions
Adjustment period: It is ok for the bridge to feel a little out of place for a few days after cementing. This is because the teeth around this area are adjusting to new forces both in between the teeth and upon biting.
Preventive Procedures: To provide optimum longevity for your restorations and to prevent future decay and supporting-tissue breakdown, please use the following home care tips: Brush after eating and before bedtime around the bridge with a soft toothbrush, especially where the crown or bridge meets the gum line (margin). At this margin area harmful bacteria can be harboured to cause decay and gum disease. An electric toothbrush is highly recommended over manual to help you keep this area clean.
Floss at least once to twice a day. Use the proxy brush, floss threader or automatic flosser to remove plaque under and around these areas to maintain good oral hygiene. On a bridge you must clean “under” as well as around the bridge. If you do not control the buildup of food debris and plaque your teeth and gums can become infected.
Water Pik™ can be used with an antibacterial, alcohol free mouthwash at the gum line and under the bridge to keep this area healthy.
Fluoride rinse is to be used before bed. Swish the fluoride rinse vigorously in your mouth for at least one minute. Do not swallow any of the rinse and do not eat or drink anything for 30 minutes.
Use a proxybrush (interdental brush) to clean around the area after each meal.
Chewing: Do not chew hard foods on the restorations for 24 hours from the time they were cemented — to attain optimum strength, the cement must mature for approximately 24 hours Also avoid eating or chewing on hard objects, food or ice Limit snacks, if high in sugar brush this area or swish with water.
Sensitivity: Do not worry about mild sensitivity to hot or cold foods. This sensitivity will disappear gradually over a few weeks. Infrequently, sensitivity last longer than six weeks.
Recare: Inadequate return for examination is the most significant reason for prostheses failure. Visit us at regular six-month examination periods. Often problems that are developing around the restorations can be found at an early stage where they can be corrected easily and will be more affordable. Waiting for a longer time may require re-doing the entire restoration.
Problems: Call us immediately if any one of these conditions occurs: If the tooth is the first tooth to hit when you bite down after a couple of days, contact us for an adjustment; a feeling of movement or looseness in the restoration; sensitivity to sweet foods; a peculiar taste from the restoration site; Breakage of a piece of material from the restoration or sensitivity to pressure.


"Healthy smiles to last a lifetime"
Contact us now to schedule an appointment.

